

Lidocaine is also the most important class-1b antiarrhythmic drug it is used intravenously for the treatment of ventricular arrhythmias (for acute myocardial infarction, digoxin poisoning, cardioversion, or cardiac catheterization) if amiodarone is not available or contraindicated.


#Lidocaine cream Patch#
The transdermal patch is also used for pain from other causes, such as compressed nerves and persistent nerve pain after some surgeries. Īn adhesive transdermal patch containing a 5% concentration of lidocaine in a hydrogel bandage, is approved by the US FDA for reducing nerve pain caused by shingles. As a local numbing agent, it is used for the treatment of premature ejaculation.
#Lidocaine cream skin#
There is tentative evidence for topical lidocaine for neuropathic pain and skin graft donor site pain. Lidocaine drops can be used on the eyes for short ophthalmic procedures. įor surface anaesthesia, several formulations can be used for endoscopies, before intubations, etc. It can be administered in multiple ways, most often as a nerve block or infiltration, depending on the type of treatment carried out and the area of the mouth worked on. Lidocaine is one of the most commonly used local anaesthetics in dentistry. Adrenaline vasoconstricts arteries, reducing bleeding and also delaying the resorption of lidocaine, almost doubling the duration of anaesthesia. Longer-acting substances such as bupivacaine are sometimes given preference for spinal and epidural anaesthesias lidocaine, though, has the advantage of a rapid onset of action. Therefore, lidocaine is suitable for infiltration, block, and surface anaesthesia. The efficacy profile of lidocaine as a local anaesthetic is characterized by a rapid onset of action and intermediate duration of efficacy. In 2020, it was the 337th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 700 thousand prescriptions.
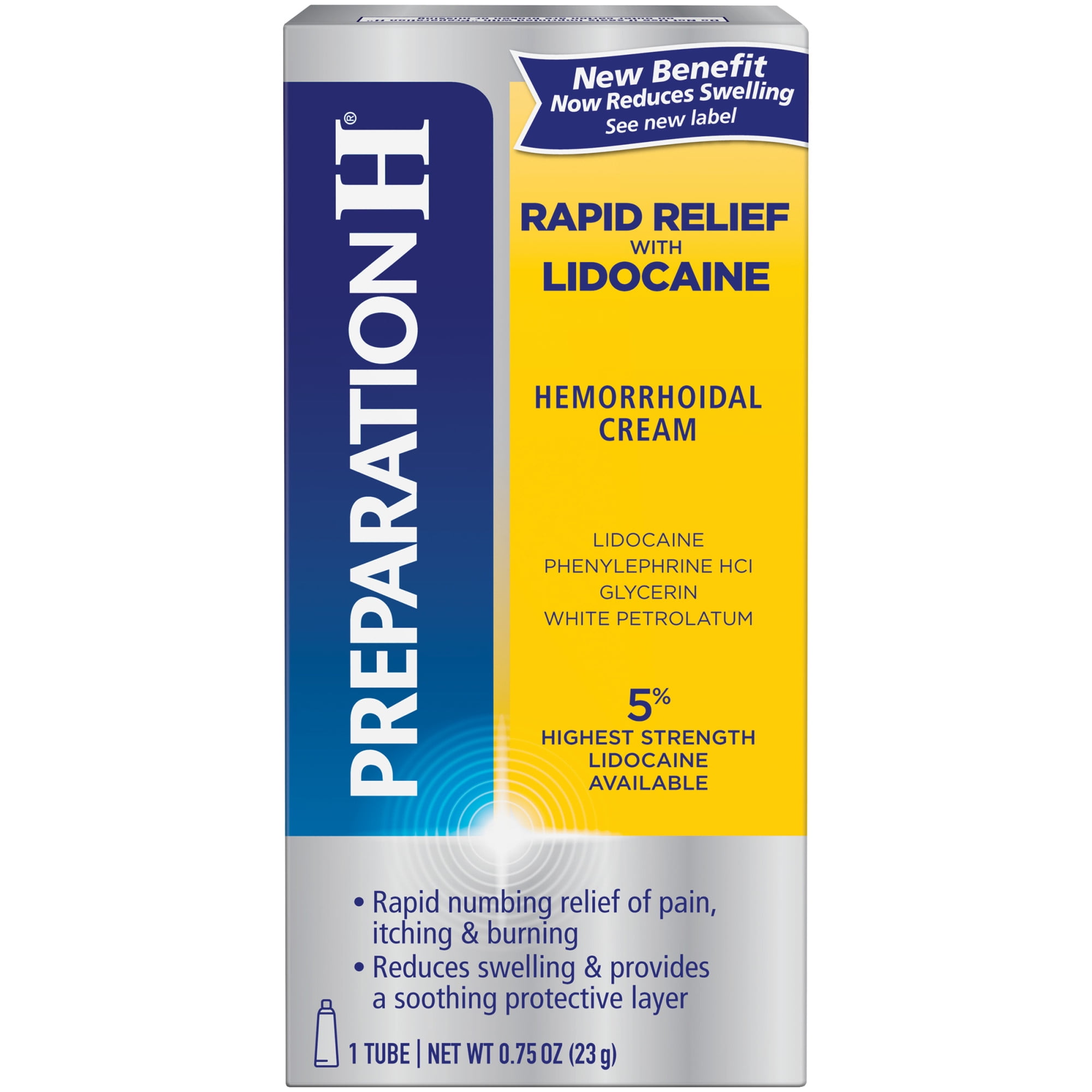
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Lidocaine was discovered in 1946 and went on sale in 1948. When injected near nerves, the nerves cannot conduct signals to or from the brain. This means it works by blocking sodium channels and thus decreasing the rate of contractions of the heart. Lidocaine is an antiarrhythmic medication of the class Ib type. It is generally safe to use in those allergic to tetracaine or benzocaine. A lower dose may be required in those with liver problems. It appears to be generally safe for use in pregnancy. There are concerns that injecting it into a joint can cause problems with the cartilage. It can cause low blood pressure and an irregular heart rate. If injected intravenously, it may cause cerebral effects such as confusion, changes in vision, numbness, tingling, and vomiting. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. Certificate approval by the Japanese government may take several weeks to process and should be received before bringing the medication or medical devices to Japan.Īll travelers entering Japan with a prescription medication, including medication that is not restricted in Japan, should consider bringing a copy of their doctor’s prescription as well as a letter stating the purpose of the drug.Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. All travelers are encouraged to check before traveling to Japan at Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) website, including reviewing FAQ, or to email who need to bring more than the MLHW’s approved quantity of medication or medical devices should obtain a “Yunyu Kakunin-sho” (importation certificate) prior to travelling, and present it with the prescription to a customs officer upon arrival in Japan. Comprehensive information is available only from the Japanese government and is subject to change without notice. Embassy and Consulates in Japan do not maintain a comprehensive list of prohibited medications or ingredients. prescription for a medicine/drug which is illegal in Japan: if you bring it with you, you risk arrest and detention by the Japanese authorities. It does not matter if you have a valid U.S. Many common medications and over-the-counter drugs in the United States are illegal in Japan. Decisions on which medications or prescription drugs can be brought into Japan are made solely by the Japanese Government and subject to control under Japan’s Pharmaceutical Affairs Law.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
